Decision tree classification in Python is one of the simplest yet most powerful techniques you can learn as a beginner in machine learning.
Did you know that decision trees are still used in top-performing Kaggle models despite being one of the oldest ML algorithms? This is because they are easy to understand, fast to train, and surprisingly accurate in many classification problems.
In this guide, you will learn exactly what decision trees are, why they matter, and how to implement them step by step using Python. If you want to build reliable ML models and increase your job-ready skills, keep reading.
What is decision tree classification in Python ?
A decision tree is a supervised machine-learning algorithm used for classification and prediction.
It works by asking a series of yes/no questions to split data into smaller and more meaningful groups.
But what does this mean for you?
It means you get a model that is easy to:
- Understand
- Visualize
- Explain to managers or clients
- Quick to train on small and medium datasets
Decision trees classify data by recursively splitting it based on features that maximize information gain or minimize impurity (like Gini or entropy).
Why decision trees matter in machine learning
Decision trees remain essential because they solve real-world problems:
- Credit scoring
- Medical diagnosis
- Fraud detection
- Customer segmentation
- Industrial process monitoring
Every split improves clarity.
Every branch represents a decision path.
Every leaf predicts a class.
For Algerian students and professionals, this method is useful because it combines theory and practice without overwhelming complexity.
How decision tree classification works
The process is simple when broken down:
1. Choose the best feature
The algorithm evaluates each feature and selects the one with the highest information gain.
2. Split the dataset
It separates the data into subsets using thresholds.
3. Repeat the process
Splits continue until the tree is “pure”.
4. Assign class labels
Leaf nodes predict the final classification.
Now let’s apply this logic using Python.
Implementing decision tree classification in Python
Here is an example using scikit-learn, the most popular ML library in the world.
📌 Step 1: Import Libraries
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score📌 Step 2: Load Dataset
data = load_iris()
X = data.data
y = data.target📌 Step 3: Split Data
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(
X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=42
)📌 Step 4: Train Decision Tree
model = DecisionTreeClassifier(criterion="gini", max_depth=4)
model.fit(X_train, y_train)📌 Step 5: Make Predictions
y_pred = model.predict(X_test)📌 Step 6: Evaluate Performance
accuracy = accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred)
print("Accuracy:", accuracy)This small code snippet shows the simplicity of using decision trees while revealing their power.
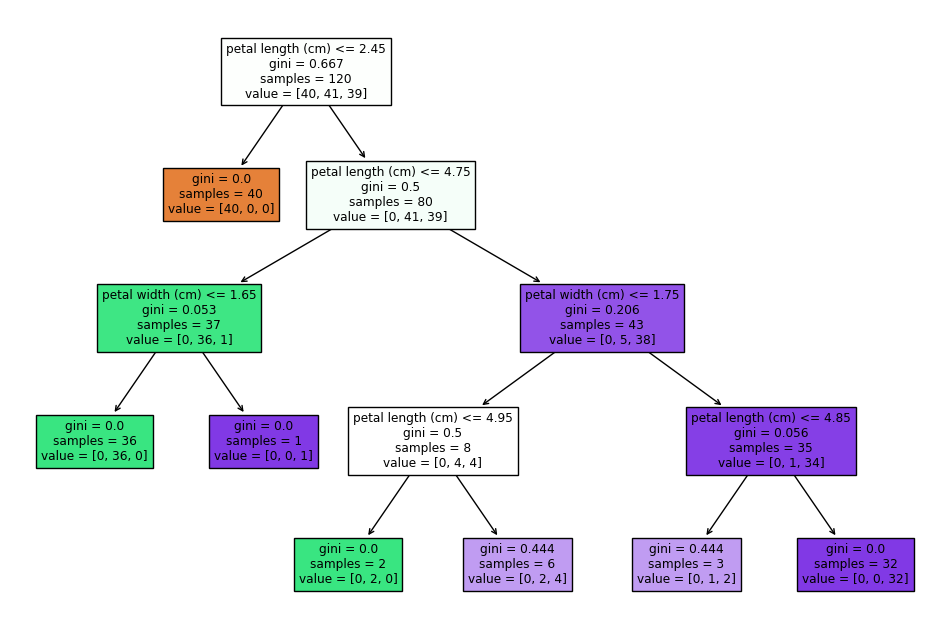
Visualizing the decision tree
Visuals help you interpret your model, especially when explaining it to teams.
from sklearn import tree
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.figure(figsize=(12,8))
tree.plot_tree(model, feature_names=data.feature_names, filled=True)
plt.show()This produces a clean, colored decision tree diagram.
Read more : Create Your First Prediction Model: House Prices Project for Beginners – Around Data Science
Decision tree pros
Decision trees offer several advantages that make them an excellent choice for beginners and professionals alike:
- Easy to understand: Even those without a data science background can follow the logic.
- Quick to train: Efficient on small to medium datasets.
- Interpretable: Each split and branch can be visualized and explained to managers or clients.
- Handles both numerical and categorical data: Flexible for many types of datasets.
- Non-parametric: No assumptions about data distribution are needed.
These pros make decision trees a practical tool for real-world tasks like credit scoring, medical diagnosis, and fraud detection.
Decision tree cons
However, decision trees also come with limitations:
- Prone to overfitting: Trees can grow very complex if not controlled with parameters like
max_depthor pruning. - Unstable: Small changes in data can lead to a completely different tree structure.
- Biased towards features with more levels: Features with many categories may dominate splits.
- Not ideal for very large datasets: Training time and memory usage can grow significantly.
- Less accurate than ensemble methods: Alone, a single tree may underperform compared to Random Forests or XGBoost.
Understanding these drawbacks helps you use decision trees effectively and decide when to combine them with other methods.
7 Bonus tips for decision tree classification in Python
To help you go further, here are 7 powerful tips that professionals use:
- Limit max_depth to avoid overfitting.
- Use entropy if you want more balanced splits.
- Enable pruning to simplify the final model.
- Normalize your data only when necessary.
- Test different criteria: gini, entropy, log_loss.
- Use GridSearchCV to find optimal hyperparameters.
- Try ensemble methods like Random Forest or XGBoost for higher accuracy.
Small adjustments often create big performance improvements.
Conclusion for decision tree classification in Python
Congratulations, you’ve made it to the end of this guide !
In this tutorial, you explored decision tree classification in Python, how it works, why it matters, and how to implement it step by step using Scikit-learn.
Hopefully, you now feel confident using decision trees to analyze your own datasets. Remember, decision tree classification in Python is one of the simplest yet most powerful techniques you can learn as a beginner in machine learning.
Start applying these skills, tune your models, and step into the world of machine learning with confidence.
Start your journey to become a data-savvy professional in Algeria.
👉 Subscribe to our newsletter, follow Around Data Science on LinkedIn, and join the community on Discord.




0 Comments