How to train, test & evaluate ML models is the foundation of every successful machine learning project, yet it remains one of the most misunderstood steps for beginners. Many models fail not because of algorithms, but because of poor evaluation strategies.
In this guide, you’ll learn a clear, practical workflow used by real-world data scientists, from dataset splitting to reliable performance metrics.
TL;DR
This tutorial explains how to correctly train, test, and evaluate machine learning models using industry best practices. You’ll learn data splitting strategies, model training workflows, evaluation metrics, common pitfalls, and hands-on Python examples suitable for beginners.
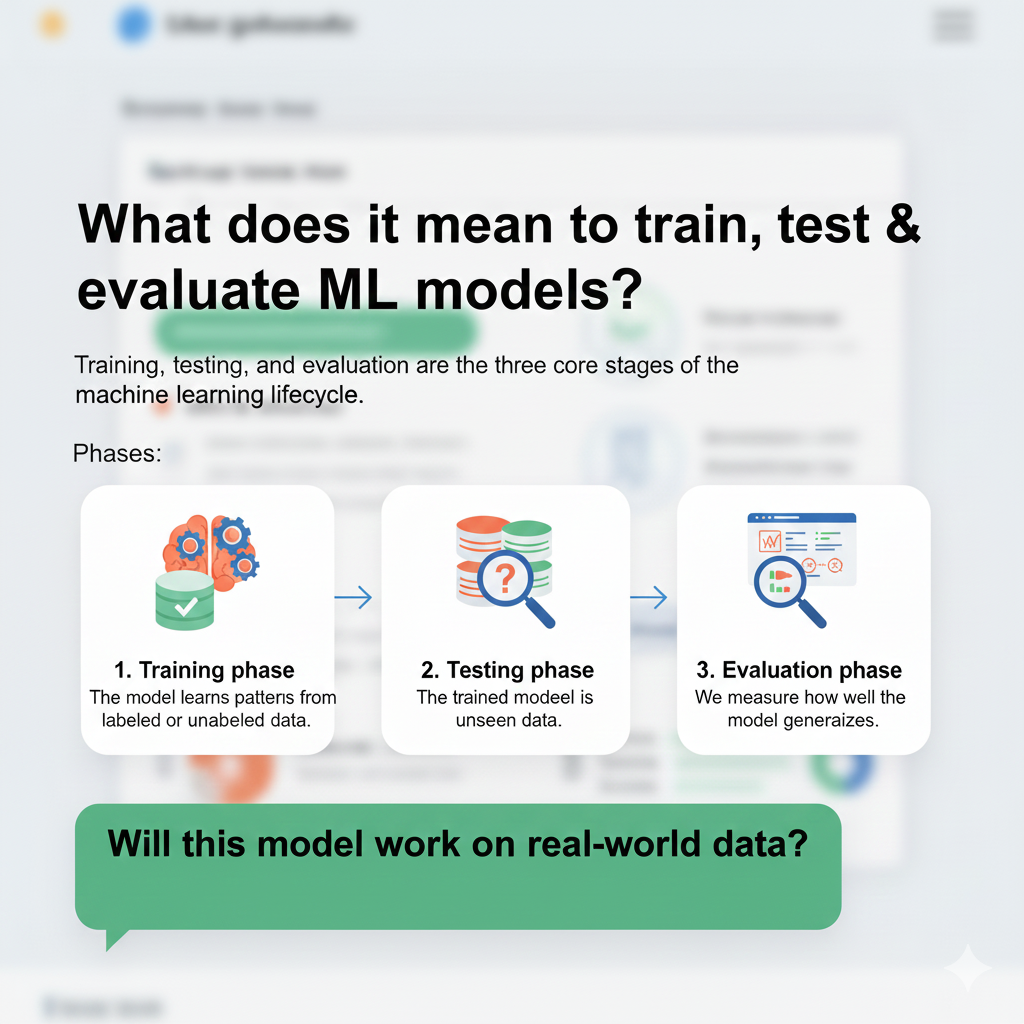
What does it mean to train, test & evaluate ML models?
Training, testing, and evaluation are the three core stages of the machine learning lifecycle.
Training phase
The model learns patterns from labeled or unlabeled data.
Testing phase
The trained model is exposed to unseen data.
Evaluation phase
We measure how well the model generalizes.
Together, these steps answer one critical question:
Will this model work on real-world data?
Check this : Understanding Data Types : A Complete Guide for Students and Professionals in Algeria – Around Data Science
Why is training, testing & evaluating ML models important?
Poor evaluation leads to:
- Overfitting
- False confidence
- Production failures
Proper evaluation ensures:
- Robust generalization
- Reproducibility
- Trustworthy predictions
For engineers and students, mastering this workflow is non-negotiable.
Typical ML workflow overview
- Data collection
- Data preprocessing
- Train-test split
- Model training
- Model testing
- Model evaluation
- Iteration & improvement
Each step directly impacts final performance.
Read more : An Excellent Machine Learning Pipeline : Don’t Search Out – Around Data Science
How to split data: train, validation & test sets
Basic split strategy
| Dataset | Purpose | Typical ratio |
|---|---|---|
| Training set | Learn patterns | 70–80% |
| Validation set | Tune hyperparameters | 10–15% |
| Test set | Final evaluation | 30–20% |
Why not train on all data?
Because evaluation must happen on unseen data to avoid bias.
Python example (scikit-learn)
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
X_train, X_temp, y_train, y_temp = train_test_split(
X, y, test_size=0.3, random_state=42
)
X_val, X_test, y_val, y_test = train_test_split(
X_temp, y_temp, test_size=0.5, random_state=42
)How to train a machine learning model
Training means optimizing model parameters using a loss function.
Example: training a logistic regression model
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
model = LogisticRegression()
model.fit(X_train, y_train)
Key elements involved:
- Loss function
- Optimization algorithm
- Model parameters
How to test ML models correctly
Testing must be:
- Done once
- Done last
- Done on untouched data
Common beginner mistake
Using test data during training or tuning.
This leads to data leakage.
How to evaluate ML models: metrics that matter
Evaluation metrics depend on the problem type.
Classification metrics
| Metric | When to use |
|---|---|
| Accuracy | Balanced classes |
| Precision | False positives matter |
| Recall | False negatives matter |
| F1-score | Class imbalance |
| ROC-AUC | Probabilistic models |
from sklearn.metrics import classification_report
y_pred = model.predict(X_test)
print(classification_report(y_test, y_pred))
Regression metrics
| Metric | Interpretation |
|---|---|
| MAE | Average absolute error |
| MSE | Penalizes large errors |
| RMSE | Error magnitude |
| R² | Variance explained |
For more details :
Cross-validation: a more reliable evaluation
Instead of one split, cross-validation uses multiple folds.
Why use cross-validation?
- Reduces variance
- More stable estimates
- Better model comparison
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score
scores = cross_val_score(model, X, y, cv=5)
print(scores.mean())
Overfitting vs underfitting
| Problem | Symptom | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Overfitting | High train, low test score | Regularization, more data |
| Underfitting | Low train and test | More complex model |
Understanding this tradeoff is essential.
Real-world example: spam detection model
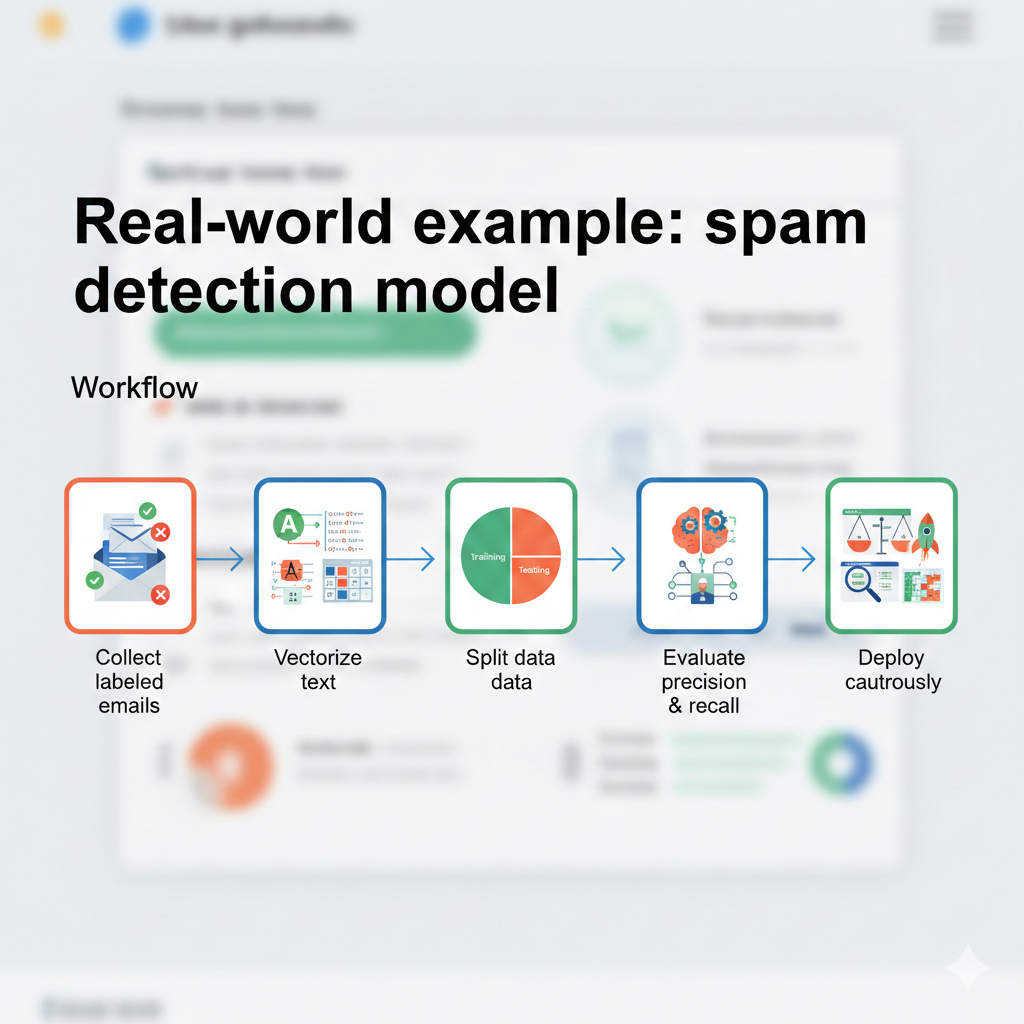
Workflow:
- Collect labeled emails
- Vectorize text
- Split data
- Train classifier
- Evaluate precision & recall
- Deploy cautiously
This mirrors industry pipelines.
Learn machine learning faster with hands-on training in Algeria
Learning how to train, test & evaluate ML models becomes much easier when theory is combined with real projects and guided practice.
If you’re based in Algeria and want structured, career-oriented training, BigNova Learning is a solid option.
Why BigNova Learning stands out:
- 📍 Located in Tala Merkha, Béjaïa
- 🧠 Focus on practical, industry-relevant skills
- 💻 Face-to-face, online, and hybrid formats
- 🎓 Ideal for students, engineers, and career switchers
Relevant courses for this topic:
- PYTHON & IA
- ALGORITHMICS
- CYBER SECURITY
- FULLSTACK WEB
- GIT & GITHUB (Workshop)
Their programs are especially useful if you want to:
- Practice model training and evaluation on real datasets
- Build ML projects for your portfolio
- Prepare for internships or junior ML roles
Common beginner mistakes to avoid
- Evaluating on training data
- Ignoring class imbalance
- Using accuracy blindly
- Forgetting random seeds
- Skipping cross-validation
7 bonus tips for how to train, test & evaluate ML models
- Always set
random_state - Visualize learning curves
- Track experiments
- Use baseline models
- Start simple
- Log metrics
- Re-evaluate after deployment
Frequently asked questions (FAQ)
What is the difference between training and testing data?
Training data teaches the model; testing data evaluates generalization.
Can I skip the validation set?
Only if using cross-validation.
How much data do I need?
More is better, but quality matters more.
Is accuracy enough to evaluate models?
No. Use task-specific metrics.
When should I retrain a model?
When data distribution changes.
What causes data leakage?
Using future or test data during training.
Conclusion for how to train, test & evaluate ML models
Mastering this workflow transforms you from a beginner into a reliable ML practitioner.
Summary:
- Split data properly
- Train with discipline
- Evaluate with the right metrics
- Avoid leakage
- Iterate continuously
The ability to train, test & evaluate ML models correctly defines successful machine learning projects.
👉 Join the Around Data Science community (Discord), subscribe to our newsletter, and follow us on LinkedIn.
Key Takeaways
- Evaluation is more important than algorithms
- Metrics must match business goals
- Cross-validation improves reliability
- Poor evaluation breaks ML systems





0 Comments